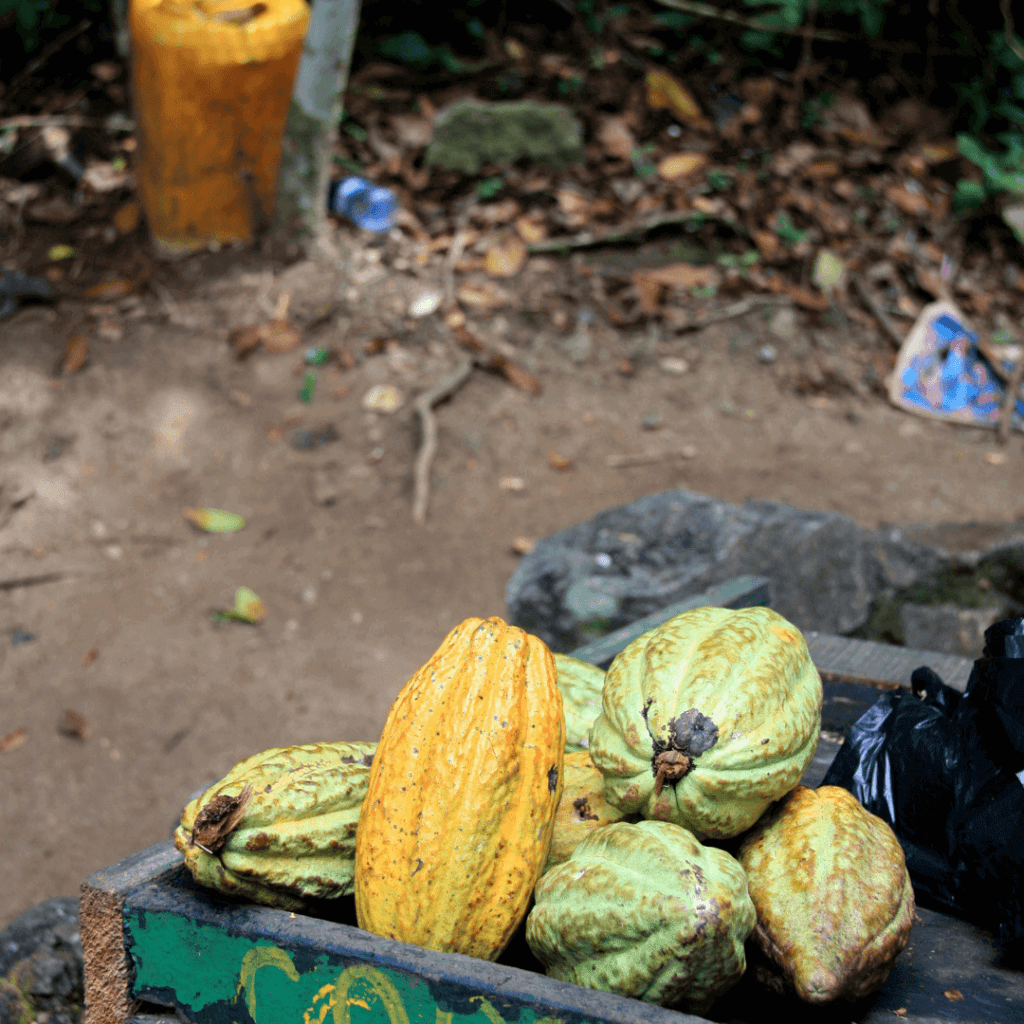Did you know that Ghana is the second biggest exporter of cocoa? When you take a walk in the forest around Moon&Star guesthouse you’ll pass a lot of cocoa farms. Assan Dickson wrote an article about cocoa for us. Since cocoa is very important to our community it might be nice for you as our guest to learn a thing or two about cocoa!
Origin of cocoa
Cocoa, Theobroma cacao, originates in the foothills of the Andes in the Amazon and Orinoco basins of South America, in Colombia and Venezuela. You can now enjoy in an endless array of products around the world, this delicacy has history that’s equally rich and compelling. The cacao tree was domesticated by the Olmecs and Mocayas (Mexico and Central America). More than 4,000 years ago, it was consumed by pre-Columbian cultures along the Yucatán, including the Mayans, and as far back as Olmeca civilization in spiritual ceremonies.
The Olmecs first discovered that the cocoa fruit was edible by observing rats eating it with gluttonous vigour. They soon realized the tree produced a fruit with a thousand flavours and nearly as many uses. Over time, the Mayansand Aztecs developed successful methods for cultivating cocoa. The cocoa bean was a monetary unit and as a measuring unit, 400 beans equaling a Zontli and 8000 equaling a Xiquipilli.
Chocolate and romance…
During their wars with the Aztecs and the Mayans, the Chimimeken people’s preferred method of levying taxes in conquered regions was in the form of cocoa beans. In its earliest forms, the Mayans used cocoa to create a ritual beverage that they shared during betrothal and marriage ceremonies, providing one of the first known links between chocolate and romance.
Introduction of cocoa in Europe
In 1524, Hernán Cortès sent a cargo of cocoa beans to the court of Charles V, who adopted the drink with added honey. Cocoa turned into profitable business, with the Spanish having a monopoly. It made it’s way to France in 1615 with the marriage of Anne of Austria, daughter of Spain’s King Philip III, with Louis XIII. In 1657, it entered England and in 1660, the English began growing cocoa in Jamaica, one of their colonies. In the 17th century, the Dutch took over a major share of the cocoa trade between America and Europe.
For a very long time, the preparation technique was very basic: hand grinding of the cocoa beans with a cylinder on a heated, slanting stone; but it changed considerably throughout the 19th century.
Cocoa has become very important to Ghana
Today cocoa has become a very important crop because it provides food, income, employment, industrial raw material and resources for poverty reduction. Besides the provision of livelihood for millions of smallholder farmers, cocoa also provides raw material for the multibillion global chocolate industries. In the article below, I will highlight on Ghana’s romance with cocoa beginning with its rich history and concluding on its historic benefits (economic and health).
My experience with Ghana cocoa
I am a son of a cocoa farmer. Indeed, I was born in a farm house located within a cocoa farm. The village was Kwakurukrom in the now Ahafo Region of Ghana. The name of the village emanated from the name of my great grandfather, Opanin Kwakuru. He had acquired several hectares of land for farming purposes. Among the farms were cocoa farms. He used his wives, children and grandchildren in cultivating the cocoa farms. This is a common practice among families growing cocoa in Ghana. I, great grandchild of Opanin Kwakuru, came to continue the legacy. Before I moved to my hometown of Banko to further my education, I assisted my parents and grandparents in the cultivation, harvesting and drying of cocoa beans.
History of Cocoa in Ghana
The history of cocoa in Ghana featured prominently in books during my early school days. In class four, I came across the name Tetteh Quarshie. This was during a book reading exercise. During that epiphanic moment I learned that Tetteh Quarshie brought cocoa to Ghana in 1870. Tetteh Quarshie was a trained blacksmith. During a missionary journey to Fernando Po, modern day Equitorial Guinea, Tetteh Quarshie hid six cocoa pods in his blacksmith tool box and shipped back into the then Gold Coast, present land Ghana. On arriving at Gold Coast, he attempted planting the first seed in Osu, a suburb of Accra, the capital city of Ghana. That failed though, with the soil type, mostly sandy and clayey.
Historic farm in Akuapem Mampong
As a missionary with the Basel Missionaries, he moved to Akuapem Mampong to continue the missionary works. Akuapem Mampong had better soil relative to Osu. Cocoa trees grow only in tropical regions +/-20º latitude from the Equator in tropical rain forests. There, the Mampong Chief gave him some acres of land. He planted his very first seed and that’s where cocoa cultivation started in Gold Coast, now Ghana. Today, the farm is still in good shape and is producing bags of cocoa for the country. In your next visit to Ghana, you may want to visit this historic farm of over 150 years. Indeed, two of the original cocoa trees planted by Tetteh Quarshie are still alive today and bearing fruits.
Cocoa farms in Ghana are Ghanaian owned
Whiles there are other contrasting stories of how cocoa came to Gold Coast (Ghana), Ghanaians and authorities in the cocoa sector believe the story of Tetteh Quarshiesector to be the most authentic. From Akwapim, cocoa farming spread to Ashanti, Brong Ahafo, Central and Western Regions, and Ghana exported her first batch of cocoa beans 80 pounds worth in 1891. By 1910-1911 Ghana was the leading producer of cocoa, producing about 40,000 tons per year. This trend continued till after independence in 1957.
Today, Ghana is the second highest producer of cocoa in the world after Ivory Coast. These two countries combined constitute more than 50% of cocoa production in the world. Cocoa farms in Ghana are mostly small size, on individual or family owned plots rarely exceeding three acres till date; there are no large plantations owned by expatriates, multinationals or corporate entities in Ghana. There are also few but very large plantations, owned by local individuals who have employed caretaker farmers in various parts of the Country where, cocoa production is favourable.
Cocoa Cultivation and Harvesting in Ghana
Cocoa grows in the forest regions of Ghana, mostly in the Ashanti, Western, Western North, Bono Ahafo, Ahafo, Bono East, Eastern and Oti regions of Ghana. The cultivation of cocoa is a laborious process. Before planting cocoa in the field the following activities should to be carried out properly;
- Land preparation
- Lining and pegging
- Spacing
- Planting temporary shade
- Mulching
- Pruning
- Pest and disease management
- Variety and sources of cocoa planting materials
- Weed management
- Soil fertility management
- Raising nursery and its management
Harvesting of Ghana cocoa
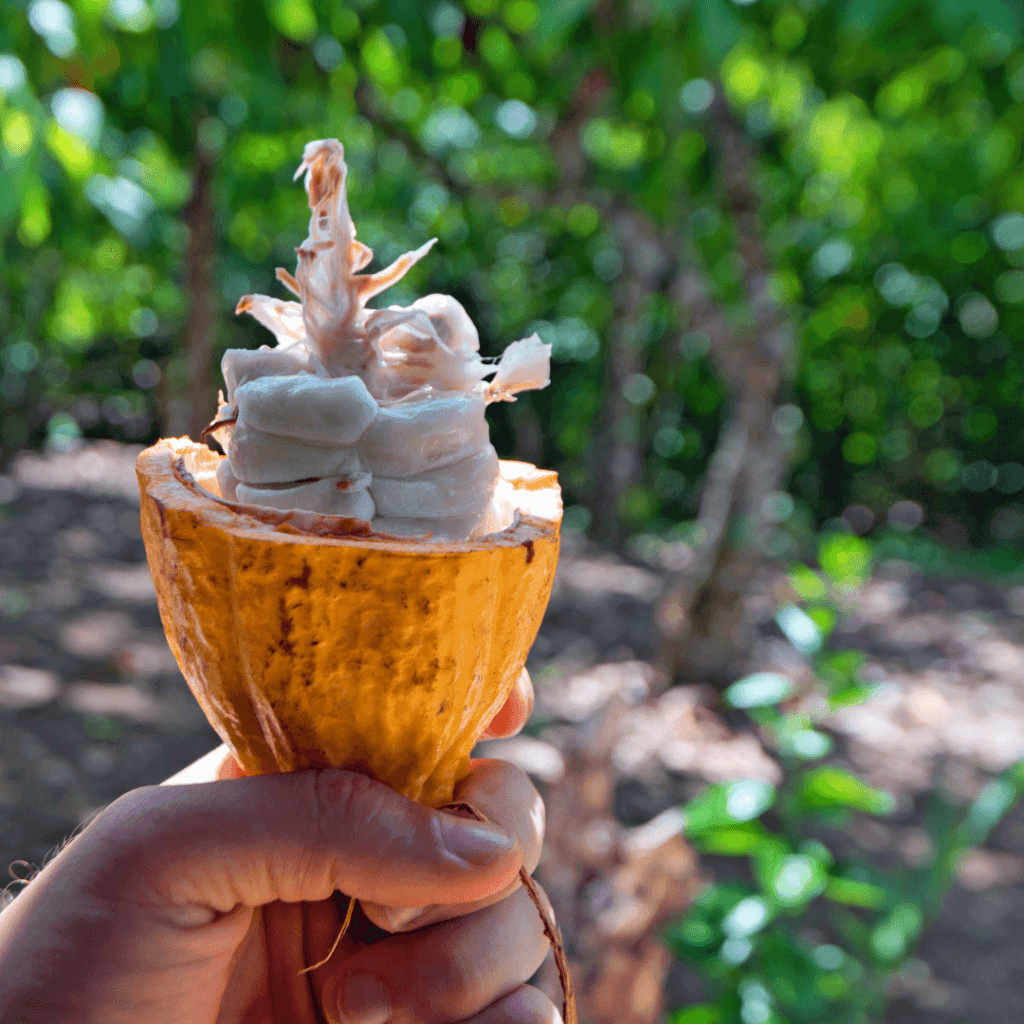
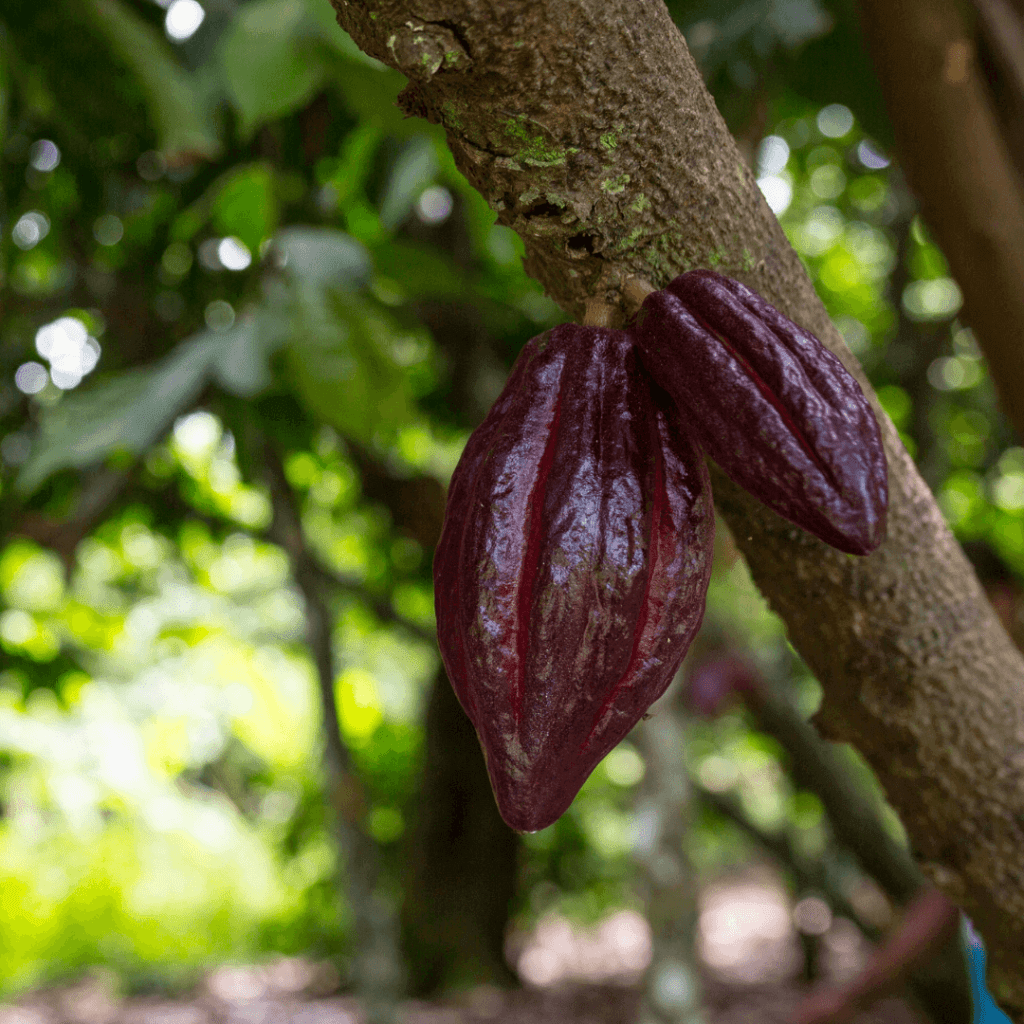
Cocoa pods are harvested regularly to prevent over-ripe pods. During harvesting, only ripe and matured pods are picked. Unripe pods cannot undergo the fermentation process, and over-riped pods also often become dry. The ripe pods are judged by their colour during harvesting. It is necessary to use sharp harvesting tools, in order not to cause damage to the cushions of the tree as damaged cushions may introduce fungi. Harvested pods are kept for about three days before breaking. Pods are usually opened using a cutlass; however, care is taken in order not to cut beans since this affects their quality. During pod breaking, beans that are cracked in pods, germinated beans and wet beans are sorted out and dried separately.
Fermenting process
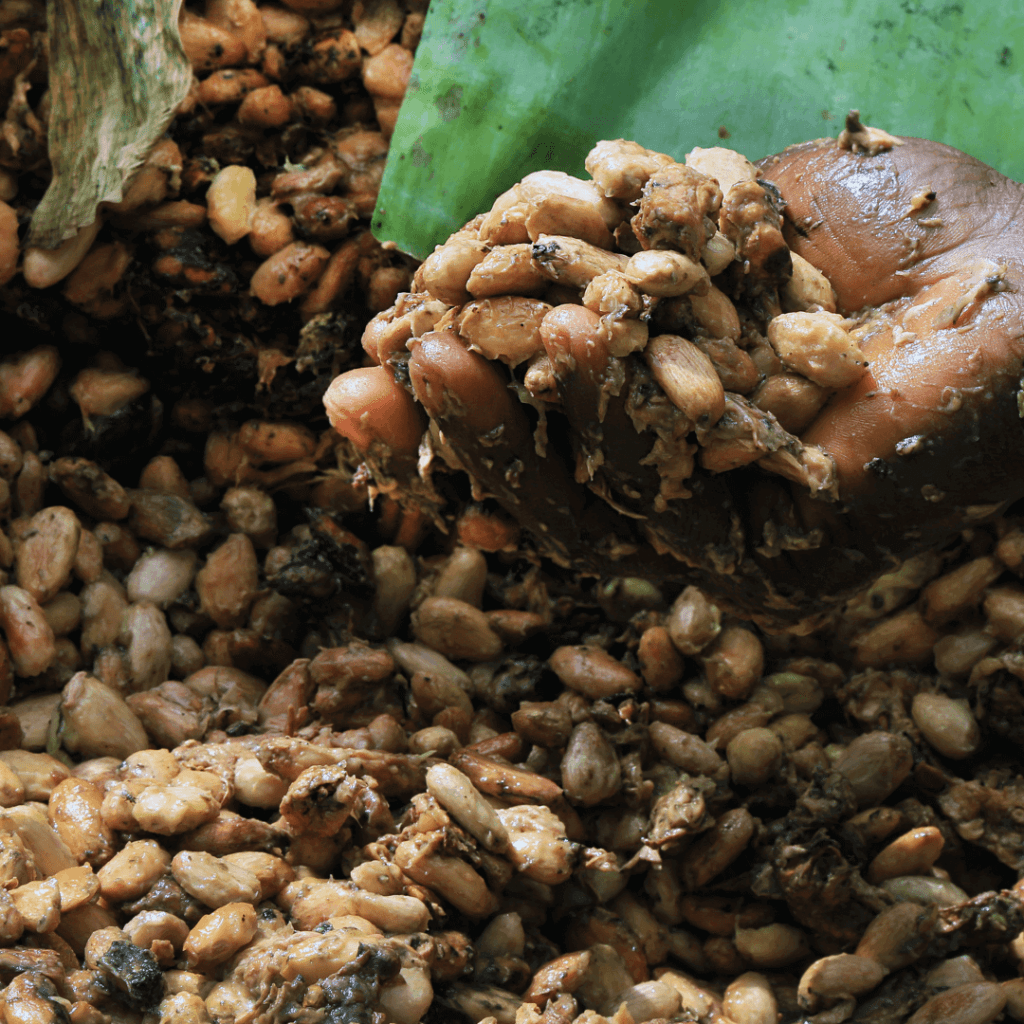
Cocoa beans are fermented in order to kill the embryo and stop germination, remove pulp to enable beans dry properly, get the proper taste, colour and flavour associated with cocoa products. In Ghana they use the heap method of fermentation. It is a cheap method that produces well fermented beans, when it is done properly. No wonder cocoa beans from Ghana are premium and best used by confeteurs for some of the best chocolate you can enjoy. With this method, short sticks are arranged in a circular form on the ground with banana leaves placed on them to overlap each other. The sticks raise the centre to enhance easy drainage of the sweating.
The farmers pour the beans in the centre and cover them with banana leaves. This is supported by placing short sticks on them from behind. Tray fermentation is done by arranging the trays in stack on a slab. The farmer places the bottom tray on a slab to avoid the ground absorbing the produced heat, to allow the sweating to drain away, and to promote air circulation. They stack the trays in piles, 3 – 12 trays high. Then they cover the top tray with banana leaves and supported with short sticks placed on them. The beans are not turned with this fermentation method and the beans ferment for five days.
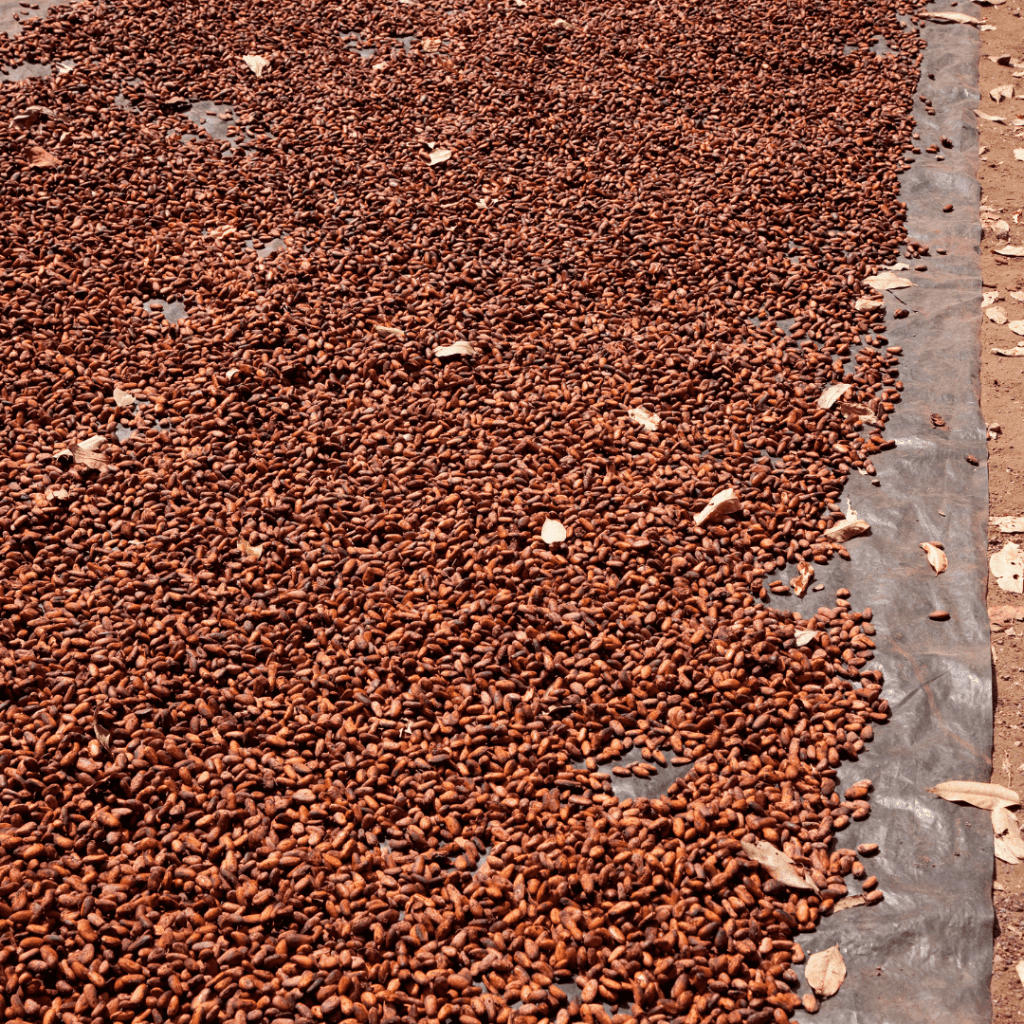
Drying of the cocoa beans
After fermentation, the water content of the beans is about 60 %, and it must be reduced to less than 7.5 % during drying to avoid spontaneous mould and bacterial growth under storage and transport. Drying of beans takes a period of about 10 -14 days depending on the atmospheric conditions and volume of beans per square area on drying mat. Well dried beans will crack easily when squeezed between the fingers and can easily be cut with a knife.
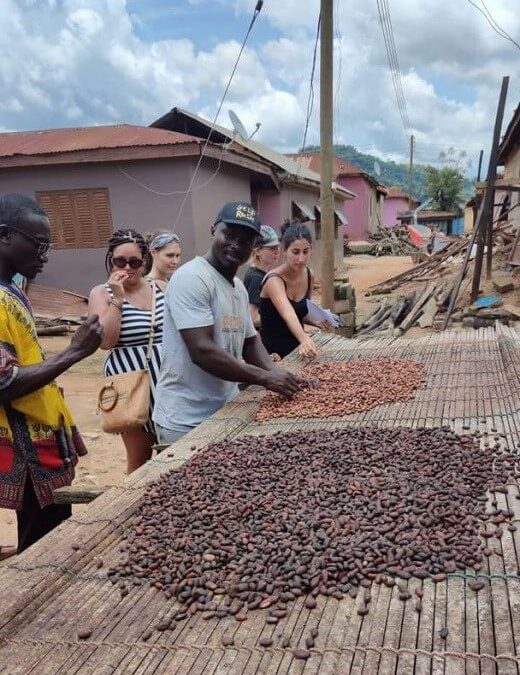
In Ghana, cocoa beans dry on the sun. Sun drying is the natural means of drying beans in the sun on raffia mats. It is simple and cheap but it is also labour-intensive and there is much concern for a stable weather condition. The mats are placed on a raised platform to protect the cocoa beans against animals and foreign materials. There is also the frequent stirring of beans on mat to facilitate drying.
It can be seen from the above that getting the cocoa beans ready for sale is a laborious process. Probably, it explains why the chocolate you consume is that costly.
Cocoa Consumption in Ghana
Once cocoa beans have been harvested, fermented, dried, and transported, cocoa processing is the next key step in preparation for commercial consumption. The beans are first transformed into cocoa liquor and then into cocoa butter or cocoa powder for producing chocolate, cosmetics and a variety of foodstuffs.
Researches have shown there are over 150 medicinal uses of cocoa. Principal among them is its cardiovascular importance. It relieves heart palpitation, strengthens the heart and blood flow thereby reducing blood pressure, reduces angina, etc. The International Cocoa Organization (ICCO) Europe consumes most of the cocoa products followed by America and Asia. Africa, the world’s major producer of cocoa beans, consumes the least of cocoa products. The raw cocoa beans are exported, before they are converted into consumable forms.
Chocolate day in Ghana
It is in this light that the Government of Ghana has instituted every 14th February as National Chocolate Day. This is to whip up the demand and consumption of cocoa products. Don’t be surprised on your visit to Ghana, you’re greeted with pure quality Golden Tree chocolate, Ghana’s premium chocolate product.
Conclusion
Cocoa is the traditional crop of Ghana. It has been around for over 150 years since it was first introduced by Tetteh Quarshie. Ghana is currently the second highest producer of cocoa, just after our neighbours Ivory Coast. It is the lifeline for several families and second major foreigner currency earner only after gold. The high quality nature of Ghana’s cocoa makes it the favourite for the chocolate world. Therefore, next time you step out to buy chocolate, find chocolates made from cocoa beans from Ghana.
This was another blog from our guestblogger Assan Dickson

Assan is a Finance Analyst, a Researcher and Teacher. He has passion for financial literacy education and has spent the last few years assisting NGOs promoting financial literacy and inclusion.
He is a Pan-Africanist and has volunteered for several black movements.
Assan is a Father and preaches on his spare time.
Assan wrote a very interesting article on volunteering and picture taking, click here to read it.
Ghana cocoa and Moon&Star guesthouse
Since we have been operating as a guesthouse we were always sad that multinationals were controlling the chocolate market. Besides the products of Golden tree there wasn’t another affordable option of cocoa products made in Ghana. But now TopChoco Ghana produces chocolate spread and cocoa powder.
If you want to know more about what Moon&Star guesthouse has to offer for you, check out the rest of our website!
Want to stay updated on Moon&Star guesthouse and our blogs, fill out the form!